
The records in hierarchical databases are organized in a treelike structure, with each level of records branching off into a set of smaller categories. In flat databases, records are organized according to a simple list of entities many simple databases for personal computers are flat in structure.
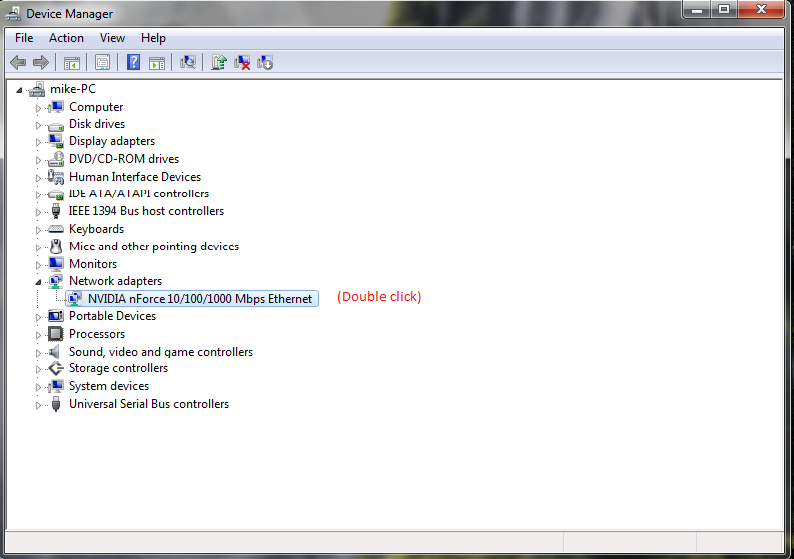
Several different types of DBMS have been developed to support these requirements: flat, hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented.Įarly systems were arranged sequentially (i.e., alphabetically, numerically, or chronologically) the development of direct-access storage devices made possible random access to data via indexes. Moreover, large business and other organizations tend to build up many independent files containing related and even overlapping data, and their data-processing activities often require the linking of data from several files. The many users of a large database must be able to manipulate the information within it quickly at any given time. Typically, the user provides a string of characters, and the computer searches the database for a corresponding sequence and provides the source materials in which those characters appear a user can request, for example, all records in which the contents of the field for a person’s last name is the word Smith. The power of a DBMS comes from its ability to define new relationships from the basic ones given by the tables and to use them to get responses to queries. Queries are the main way users retrieve database information. Using keywords and various sorting commands, users can rapidly search, rearrange, group, and select the fields in many records to retrieve or create reports on particular aggregates of data.ĭatabase records and files must be organized to allow retrieval of the information. Although database is applied loosely to any collection of information in computer files, a database in the strict sense provides cross-referencing capabilities. Records are also organized into tables that include information about relationships between its various fields. Fields are the basic units of data storage, and each field typically contains information pertaining to one aspect or attribute of the entity described by the database. The information in these files may be broken down into records, each of which consists of one or more fields. Hack into this quiz and let some technology tally your score and reveal the contents to you.Ī database is stored as a file or a set of files.
#Pc idatabase how to

From tech to household and wellness products.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
